Testing
Choyling's Blog
Thursday, January 24, 2019
Wednesday, July 4, 2018
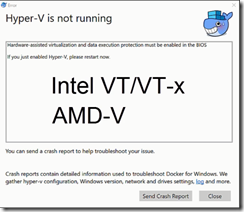
Getting Started with Docker
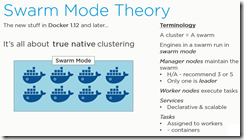
Swarm
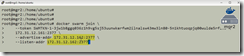
Different tokens are used to join a manager node and a worker node.
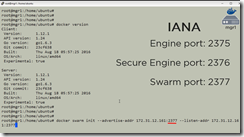
Very Important: specify the advertise address and listen address
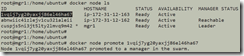
To promote a worker node to manager node. Can do this from any manager node.
After promoting a worker node to manager node, the Manager Status changed from empty (no value) to ‘Reachable’. Empty/no value means it’s a worker node.
Services
Running services in the Swarm
To create service
Shut down one of the nodes
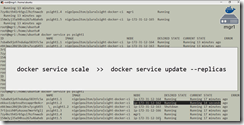
To scale the services
Docker automatically create new containers and distribute the containers among the availablAte nodes when scaling.
Adding new nodes to the Swarm doesn’t cause the Swarm to re-balance the load. * This behavior might change in the future.
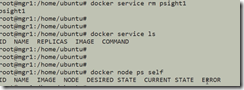
To remove service:
To create an Overlay network:
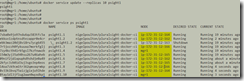
Create a new service with 12 replicas:
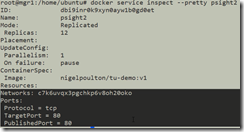
To inspect a services:
Can add option at docker service create command for service update, i.e. update the task (container) 2 at a time, wait for 10 minutes, then update another 2 tasks (containers).
To make it easy to read:
Stacks and Bundles
Thursday, October 5, 2017
User Records
- User record is required to login.
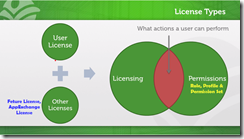
- 1 Person = 1 User = 1 User License
- User record can not be deleted, but can be deactivated.
- Records in SF can be assigned to:
- Active user
- Queue
- Freeze User –
- To prevent user to login, but the user is still active. Best to freeze user to perform maintenance when you don’t want user to login temporary.
- Someone left the company, need to deactivate user, but can’t deactivate due to the user is tied to some workflow rules/other rules. Best to freeze the user to prevent login immediately, delete the rules/sort out other things, then deactivate the user.
Tuesday, September 5, 2017
Data Security
Org, Object, Record, Field, Folder Security
Profile
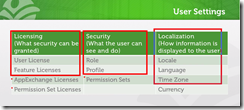
- A profile is a collection of permissions and settings that is instrumental in determining a user’s functional access (apps, tabs, object-level permissions), how information is displayed to the user (page layouts, record types, field-level security), and a wide range of other permissions.
- Each user must be assigned one profile.
- Standard profile – limited changes can be made. Can’t be deleted.
- Custom profile – fully customizable. Can be deleted.
- It’s best to assign all users to custom profile.
Permission Sets
Roles
- https://certifiedondemand.com/security-model/roles/
- You need both object and record level security to perform an action.
- Profile grants object level access
- OWD, record ownership, and role hierarchy grant record level access
Groups
- https://certifiedondemand.com/security-model/groups/
- Group is comprised of users, roles and/or other groups.
- Public Groups – created & maintained by admin, can be referenced in orq-wide configuration (e.g. sharing rules).
- Personal Groups – created & maintained by users, can only be referenced in selected configurations (e.g. Outlook contact sync).
- Common user cases:
- Sharing access to records or folders with named users (this requires a public group) – User is not an option.
- Sharing access to resources (folders, etc) to same collection of users within specified roles. e.g. sharing 3 folders with 2 roles.
- Important:
- There is no way to monitor where groups are referenced (e.g. you have to view each individual report folder, sharing rules, etc.). For this reason, make sure to have a clear documentation and usage strategy for groups (or at a minimum, a very clear naming convention).
- When groups are referenced in sharing rules, “Grant Access Using Hierarchies” can be extended to group access.
Manual Record Sharing & Auditing
- https://certifiedondemand.com/how-to-verify-salesforce-record-access/
- In general, if OWD of an object = Private or Public Read Only ==> sharing button will be displayed (if added to page layout).
- Exception: Some objects (account) may have sharing button exposed, depending on the sharing setting.
- Manual record sharing - can share record with groups, roles, users.
- Must have ‘Full Access’ to the record to do manual sharing.
Ref:
https://certifiedondemand.com/overview-of-salesforce-security-model
Thursday, August 17, 2017
Process Automation – Approval Process

- Initial submission actions:
- locks the record
- Other submission actions include sending email alert, updating a field on a record, creating task, sending an outbound message.
- Approval Step – assign users (approvers).
- Final Approval Actions
- These actions occur only a record is approved & no further approval needed.
- Changes the record status to ‘Approved’, unlock the record, notify employee who submit the request of new position.
- Approval process must be activated to make it available to the users.
Discount Approval Process – 2 Steps
Chatter is not available in Developer Org – so can’t set up Chatter message for approval updates.
Hands-on Training: Streamline Requests with Approval Processes https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0u3L8JIJjbE
Wednesday, June 14, 2017
Process Automation - SalesForce Workflow Rule
- Use Process Builder rather than Workflow, if possible.
- A workflow rule is the main container for a set of workflow instructions. These instructions can always be summed up in an if/then statement.
- Workflow rule example: If an account is created or updated and it’s located in Texas, you want Salesforce to automatically perform certain actions. Here’s how that if-statement breaks down into workflow rule criteria.
- An account (object)
- is created or updated (evaluation criteria) and
- is located in Texas (rule criteria)
Every workflow rule is directly associated with one and only one object.
- Action:
- Immediate actions
- Time-dependent actions (before or after)
- If you selected “created or edited” for your evaluation criteria, you can’t add time-dependent actions. You can monitor and cancel pending time-dependent actions from Time-Based Workflow in Setup.
- Time trigger:
- trigger action before or after
- Now = Rule Trigger Date (e.g. 7 days from now = 7 days after rule trigger date.
- Workflow Action can be saved & reused:
- Click Add Workflow Action | Select Existing Action.
What is Workflow?
Workflow automates the following types of actions based on your organization's processes:
 Tasks—Assign a new task to a user, role, or record owner.
Tasks—Assign a new task to a user, role, or record owner.
 Email Alerts—Send an email to one or more recipients you specify.
Email Alerts—Send an email to one or more recipients you specify.
 Field Updates—Update the value of a field on a record.
Field Updates—Update the value of a field on a record.
 Outbound Messages—Send a secure, configurable API message (in XML format) to a designated listener.
Outbound Messages—Send a secure, configurable API message (in XML format) to a designated listener.
 Assign follow-up tasks to a support rep one week after a case is updated.
Assign follow-up tasks to a support rep one week after a case is updated.
 Send sales management an email alert when a sales rep qualifies a large deal.
Send sales management an email alert when a sales rep qualifies a large deal.
 Change the Owner field on a contract three days before it expires.
Change the Owner field on a contract three days before it expires.
 Trigger an outbound API message to an external HR system to initiate the reimbursement process for an approved expense report.
Trigger an outbound API message to an external HR system to initiate the reimbursement process for an approved expense report.
 Criteria that cause the workflow rule to run.
Criteria that cause the workflow rule to run.
 Immediate actions that execute when a record matches the criteria. For example, Salesforce can automatically send an email that notifies the account team when a new high-value opportunity is created.
Immediate actions that execute when a record matches the criteria. For example, Salesforce can automatically send an email that notifies the account team when a new high-value opportunity is created.
 Time-dependent actions that queue when a record matches the criteria, and execute according to time triggers. For example, Salesforce can automatically send an email reminder to the account team if a high-value opportunity is still open ten days before the close date.
Time-dependent actions that queue when a record matches the criteria, and execute according to time triggers. For example, Salesforce can automatically send an email reminder to the account team if a high-value opportunity is still open ten days before the close date.
Wednesday, June 7, 2017
Process Automation
- SF provides 4 automation tools:
- Workflow
- Process Builder
- Visual Workflow – collect info
- Approvals
- The only thing you can do with workflow that you can’t do with processes is send outbound messages without code.
- Cloud Flow Designer – for more complex workflow logics.
- Can reorder criteria, but not action. Need to delete & recreate action to reorder.
- Scheduled action – only if process starts with creating a record.
- Automated process consist of:
- Criteria
- Actions – Immediate or scheduled
Process Builder
- Click Advanced and select Yes (6).When you select this option, the process ignores record changes that aren’t relevant to your defined criteria. For example, if a user edits the record by adding a description, the process won’t execute the associated actions. Note: This setting isn’t available if:
- Your process starts only when a record is created.
- Your process starts when a record is created or edited and the criteria node doesn’t evaluate any criteria.
- The criteria node evaluates a formula, but the formula doesn’t include a reference to the record that started the process.
- Your process uses the Is changed operator in a filter condition.